Introduction
- There is a possibility of a global economic recession due to the violent confrontation between Israel and Iran. According to some scholars, due to the increased confrontation, the possibility of closure of the Strait of Hormuz (a narrow passage between Iran and Oman that is an important route for global oil transportation, where containers carrying crude oil reach North America, Asia, Europe, and various parts of the world from the Gulf region) has increased, due to which the risk of global recession is continuously growing due to the increase in oil prices.
- In this, producing countries like Saudi Arabia, Russia, Oman, and other Gulf countries will benefit, but importing countries like India, China, South Africa, the European Union, etc. According to Goldman Sachs, in the worst-case scenario related to obstructions in the Strait of Hormuz, oil prices can go above $100-120 per barrel.
- As a result, production costs will rise, leading to higher prices for energy-intensive goods such as food, clothing, and chemicals.
Impact on the United States and Latin America
- If seen in the context of geopolitics, the involvement of America (good relations with Israel) in the conflict between Israel and Iran can lead to instability in the Gulf region, which can lead to proxy war, regional angles, and agitations on nuclear issues, which will not be good for that region and for America’s energy supply.
- If seen from the angle of oil supply, it has reduced its dependence on Gulf countries, for example, importing ~6.2 million bpd with less than 10% from the Persian Gulf. The blockade on the Strait of Hormuz will change global prices, which will indirectly affect US domestic fuel prices, even though there is no direct threat to supply.
- An Israel and Iran war may put US trade (trade between Israel and the US—$50 billion) and investments at risk—US companies in Israel and Gulf countries, including defense technology, cybersecurity, and biotech sectors.
- US companies operating in Israel, Iraq, or Gulf countries may face missile/drone threats (e.g., Iranian proxies), insurance and shipping disruptions, and cybersecurity risks (hackers linked to the Iranian state).
- Demand for US weapons (e.g., missile defense systems like Iron Dome and THAAD) may increase.
- The Israel and Iran war has a high chance of causing energy instability. According to Goldman Sachs’ estimates, in similar crises, the war could lead to oil prices reaching $100-$120 per barrel. As a result, a $10/barrel increase in fuel costs will add $30 billion to America’s annual fuel costs, and the inflation rate could increase by 0.3-0.5%.
- America may have to face some strategic consequences in the war between Israel and Iran, such as America maintaining military bases in the entire region: Qatar, Bahrain, UAE, Iraq, Syria, and Jordan. The chances of damage to these bases increase, protecting shipping lanes and stopping Iran’s allies (e.g., Hezbollah, Houthis). https://www.wilsoncenter.org/article/who-are-yemens-houthis
- America’s entry into the Israel and Iran war can give political space to Russia and China in this region.
Impact on China
- China can suffer a lot in the energy region due to geopolitical reasons in the war between Israel and Iran. If war breaks out, regional supply chains, oil routes, and geopolitical balances would be severely affected, particularly for China, which maintains close energy ties with Iran while maintaining diplomatic ties with Israel.
- China is the world’s largest oil importer, importing more than 11.3 million barrels per day (bpd) by 2023. About 40% of China’s crude oil imports come from the Middle East.
- According to historical examples such as the Gulf War (1990-91) and the 2003 Iraq invasion, a full-blown war could push oil prices to $130-$150/barrel.
- From the angle of investment risk and trade, China-Iran trade was almost $16 billion, with China exporting machinery, chemical products, and electronics to Iran.
- Sanctions and instability in the region will make it difficult for B2B to function and operate smoothly, especially the oil-to-technology barter system.
- China-Israel trade is expected to decline from $21.4 billion in 2022. China has invested in numerous projects in Israel, including the Haifa Port and the Tel Aviv Light Rail Project.
- Iran is a key country in China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) program, which connects China to the Middle East through the China-Central Asia-Iran corridor.
- This war can put China’s infrastructure and Chinese personnel at risk. This could delay or cancel the 25-year Iran-China agreement (worth $400 billion).
- An Israel and Iran war can lead to volatility in energy prices, like:
- In the Gulf War (1990-91), oil prices rose from $17 to $39 per barrel in a few weeks, and in 2019, the Abqaiq (Saudi oil facility) attack caused Brent crude to jump 14.6% overnight.
- According to IMF and World Bank estimates, China may face an economic shock if oil prices rise by $10 per barrel; then China’s GDP growth may reduce by 0.1-0.2%.
- China’s diplomatic and strategic thinking is running under a plan, which is to support Iran and those countries due to anti-American sentiment.
- Supports the organizations (Hezbollah, etc.) nurtured by ISIS but values stable relations with Israel, especially in trade and innovation.
Impact on Europe
- Due to the lack of energy supply due to the war between Israel and Iran and the increase in the price of oil and gas, inflation may increase in Europe. Europe may face a double blow because the euro is already booming due to the reduction of energy dependencies from Russia, and now, due to the increase in stability in the Middle East, the inflation rate will increase. Recently, Germany’s DAX and France’s CAC40 markets have sunk by 1%. But defense industrial shares (BAE Systems, Airbus, etc.) have increased.
- Central banks in G-7 countries are currently cutting interest rates, such as the Bank of England, which has recently reduced the base interest rate of the United Kingdom to 4.25 percent, although the US Federal Reserve has stopped the reduction.
Impact on Africa
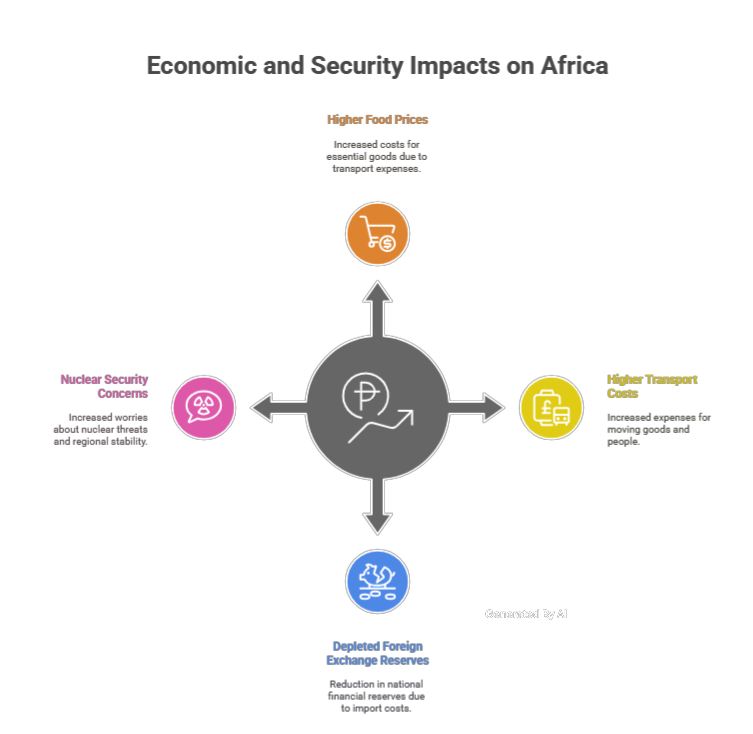
- Most of the countries in the African region import oil. Due to the high cost of oil, the prices of diesel and gas will increase, which will increase the prices of food and transport, which will lead to a decline in foreign exchange reserves.
- The African Union has raised concerns, and South Africa has expressed concern over nuclear security, while Nigeria has expressed concern over the stability of the Middle East.
Impact on Gulf Countries (Middle East)
- The economy of the oil-exporting countries of the Gulf (Saudi Arabia, UAE, Qatar, Kuwait, etc.) mostly runs on oil exports. If Israel attacks Iran’s oil infrastructure during the Israel-Iran war, then Iran, along with its allies (Iraq and the Houthi militia of Yemen), can attack the oil infrastructure of the Gulf countries.
- Currently, OPEC (led by Saudi Arabia) can meet the shortage of Iranian oil, but if the war between Israel and Iran does not stop and this war spreads to the Gulf countries, then a global oil crisis will arise.http://opec.org/
Impact on India
- In the geopolitical context, the instability in the Middle East region due to the war between Iran and Israel can cost India a lot because this is a region of great strategic and economic importance for India.
- Iran has been a traditional ally, a major energy supplier, and a major partner in regional connectivity projects like Chabahar Port.
- On the other hand, Israel is an important defense, intelligence, and technology partner. A conflict can force India to balance complex relations while handling the impact on its economy and expatriate community in the Gulf.
- India imports at least 80-85% of its crude oil, due to which the energy region becomes very sensitive.
- India’s major suppliers are Iraq, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Russia, and 60% of oil comes from the Middle East alone.
- Iran was India’s third-largest crude oil supplier (~24 million tons) earlier, but imports stopped after 2019 due to US sanctions.
- 80% of India’s oil comes through the Strait of Hormuz.
- If the war between Israel and Iran escalates, India’s energy security, shipping costs (insurance surcharges), and refinery operations in western India (for example, Jamnagar, the world’s largest oil refinery) could be affected.
- Choking the Strait of Hormuz could add $10-15 billion/month to India’s import bill.
- As of 2022-23, India’s trade with Gulf countries is $184 billion, and trade with Israel is ~$10.1 billion (mainly defense tech, diamonds, and agri-tech).
- There are ~9 million NRIs from India working in Gulf countries in various sectors like construction, energy, healthcare, and retail (largely staffed by Indians). If the Israel & Iran conflict escalates in the Middle East, their lives could be at risk.
- Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) impact. Although BRI is a China-led initiative, India also sees Chabahar port as a strategy to counter the Iran-China project, which could be affected in a war between Israel and Iran. There are several ambitious projects underway in Iran that could be impacted, such as the feasibility of the Chabahar-Zaranj-Delaram highway, India’s broader connectivity ambitions in Central Asia, and India’s plan to bypass Pakistan through the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC).
- Volatility in energy prices has been observed from time to time, such as
- The Gulf War (1990-91) caused crude oil prices to rise from $17 to $39/barrel.
- In 2019, Iran-US tensions caused prices to rise by 14% in a single day.
- A full-blown conflict could push Brent crude to $130–$150 per barrel.
- India’s fiscal deficit could increase by 0.5-1% of GDP due to the Israel and Iran war. Inflation (CPI) may increase by 1-2 percentage points, and the rupee is likely to depreciate due to increased foreign currency outflows.
- India has deep strategic ties with Israel in the diplomatic and strategic fields, and Israel is India’s second-largest supplier in defense fields such as drones, missiles, radars, and AI-based systems.
Conclusion
- A potential war between Iran and Israel will not remain just a regional conflict but can seriously impact global energy security, trade routes, geopolitical stability, and economic balance. Major powers like the US, China, and India will be directly or indirectly affected by this conflict.
- While the US will face strategic military and energy costs, China will face disruptions in energy supplies, investment risks, and BRI projects. This crisis is particularly sensitive for India, as it is highly dependent on the Middle East for energy, trade, and migrant labor.
- Factors like rising energy prices, rising inflation, trade instability, and diplomatic balance can make India’s economic and strategic position challenging.
